Annuity Calculator
Results
Ending Balance:
Total Contributions:
Total Interest Earned:
Annual Schedule
Monthly Schedule
Annuity Explained: Meaning, Types, Examples, Formulas, and Annuity Calculator
An annuity is one of the most widely used financial concepts in retirement planning, investment growth, loans, and insurance products. Whether you are saving for retirement, investing regularly, or calculating future value, understanding annuities is essential for making informed financial decisions.
This guide explains what an annuity is, how annuities work, types of annuities, annuity formulas, real-world examples, and factors that affect annuity growth, along with common questions people search online.
What Is an Annuity?
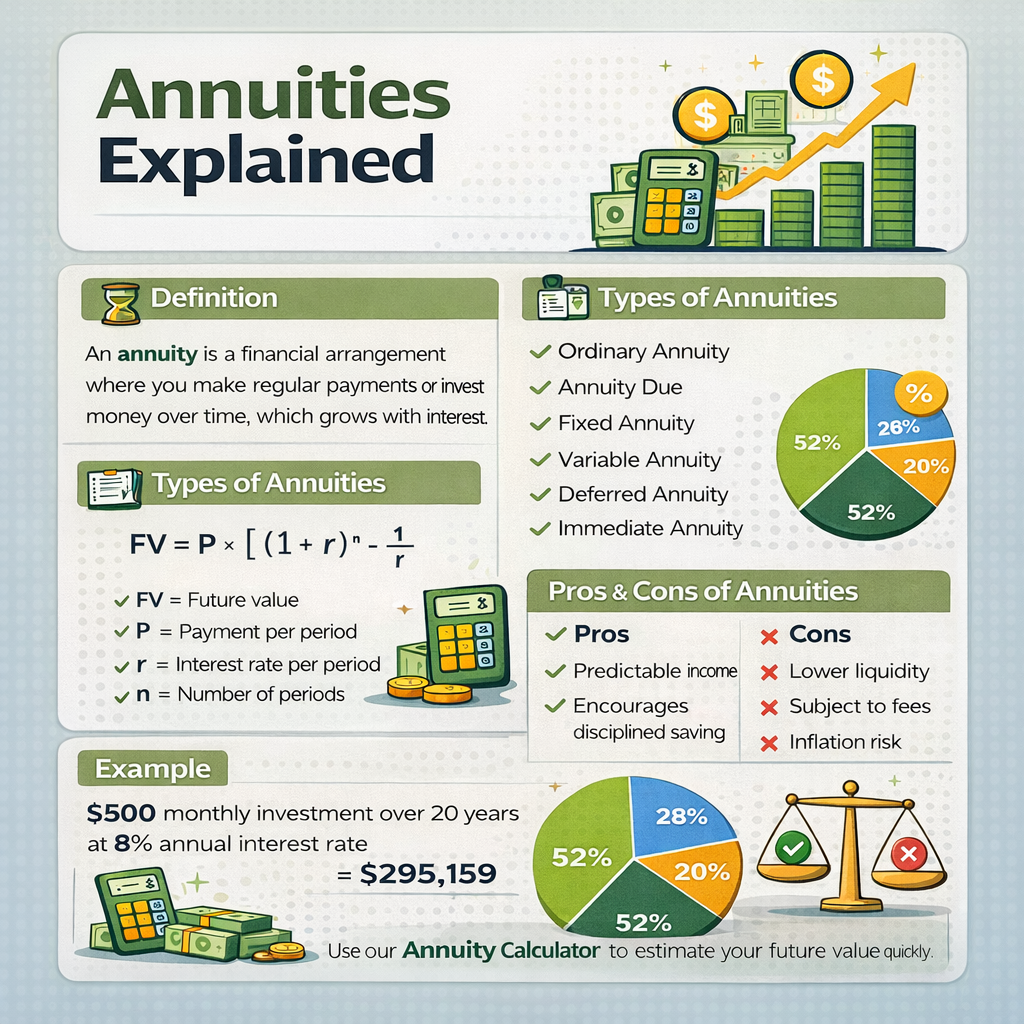
An annuity is a financial arrangement that involves a series of equal payments made at regular intervals over time. These payments can be either investments (money going in) or payouts (money coming out).
In simple terms:
You invest or deposit money regularly
The money earns interest over time
The final value depends on contribution amount, interest rate, and time
Annuities are commonly used for:
Retirement savings
Pension plans
Insurance products
Loan repayment calculations
Investment growth projections
How Does an Annuity Work?
An annuity works by combining regular contributions with compound interest. Each payment is added to the balance, and interest is calculated on the total amount accumulated so far.
Key components of an annuity:
Starting principal – initial investment amount
Periodic contributions – monthly or annual payments
Interest rate – growth rate applied to the balance
Time period – duration of the annuity
Payment timing – beginning or end of each period
The longer the investment period and the higher the interest rate, the greater the annuity’s final value.
Types of Annuities
Understanding different types of annuities is crucial because the calculation and outcome vary depending on structure.
1. Ordinary Annuity (Immediate Annuity)
In an ordinary annuity, payments are made at the end of each period.
Examples:
Loan repayments
Rent payments
Credit card payments
This is the most common type of annuity used in finance.
2. Annuity Due
In an annuity due, payments are made at the beginning of each period.
Examples:
Retirement savings plans
Insurance premiums
Monthly investment plans
Because payments are made earlier, annuity due typically results in a higher final value than an ordinary annuity.
3. Fixed Annuity
A fixed annuity offers:
Guaranteed interest rate
Predictable growth
Lower risk
It is commonly used by conservative investors and retirees seeking stable income.
4. Variable Annuity
A variable annuity:
Depends on market performance
Has higher potential returns
Carries higher risk
Returns fluctuate based on underlying investment funds.
5. Deferred Annuity
In a deferred annuity:
Payments are delayed until a future date
Money grows during the accumulation phase
Often used for long-term retirement planning.
6. Immediate Annuity
An immediate annuity:
Begins payouts shortly after investment
Used to convert savings into regular income
Annuity Formula
The annuity formula calculates the future value of regular payments with interest.
Ordinary Annuity Formula
FV = P × [ ( (1 + r)^n − 1 ) / r ]
Annuity Due Formula
FV = P × [ ( (1 + r)^n − 1 ) / r ] × (1 + r)
Where:
FV = Future value of annuity
P = Payment per period
r = Interest rate per period
n = Number of periods
Factors That Affect Annuity Growth
Several factors influence how much an annuity grows:
1. Interest Rate
Higher interest rates significantly increase the final value due to compounding.
2. Investment Duration
Longer time horizons result in exponential growth.
3. Contribution Frequency
Monthly contributions generally outperform annual contributions due to more frequent compounding.
4. Payment Timing
Annuity due grows faster than ordinary annuity.
5. Initial Principal
A higher starting balance increases total returns.
Advantages of Annuities
- Predictable income
- Encourages disciplined saving
- Reduces market timing risk
- Ideal for retirement planning
- Flexible contribution options
Disadvantages of Annuities
- Lower liquidity
- Fees in some insurance-based annuities
- Inflation risk with fixed annuities
- Complexity in certain products
Annuities in Retirement Planning
Annuities play a major role in retirement because they:
Provide stable income streams
Reduce longevity risk
Help manage post-retirement cash flow
Supplement pensions and social security
Many retirees use annuities to ensure income lasts throughout their lifetime.
Tax Treatment of Annuities (USA)
In the United States:
Contributions may be tax-deferred
Earnings are taxed upon withdrawal
Early withdrawals may incur penalties
Tax rules vary based on annuity type and provider.
our Annuity Calculator
Annuity calculator is a powerful financial planning tool that helps individuals estimate future income, payments, and overall returns from annuity investments. Whether you are evaluating an annuity calculator immediate option to determine regular payouts starting right away, or using an annuity calculator FV to calculate the future value of long-term contributions, this tool provides accurate projections in seconds. For long-term financial security, an annuity calculator retirement is especially useful in planning guaranteed income during retirement by comparing different payout structures and investment durations. By eliminating manual calculations, this calculator delivers precise results and supports informed decisions for retirement and income planning.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is an annuity a good investment?
Annuities are suitable for long-term, low-risk income planning but may not fit aggressive investment strategies.
What is the difference between annuity and interest?
Interest is the growth rate, while an annuity is the structured payment system that earns interest.
Can annuities lose value?
Fixed annuities are stable, while variable annuities can lose value due to market fluctuations.
Are annuities better than mutual funds?
Annuities prioritize income stability, while mutual funds focus on growth potential.
Final Thoughts
Annuities are powerful financial tools for saving, investing, and retirement planning. By understanding annuity types, formulas, and factors affecting growth, you can make smarter financial decisions and maximize long-term wealth.
Using an annuity calculator allows you to visualize results, compare scenarios, and plan confidently for the future.
Popular Calculator Tools
- Interest Rate Calculator
- Period Calculator
- Loan Calculator
- Ovulation Calculator
- Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) Calculator
- Blood Pressure Calculator
- Pregnancy Calculator
- Conception Calculator
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Pregnancy Conception Calculator
- Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) Calculator
- Fat Intake Calculator
- Annuity Payout Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Sales Tax Calculator
- VAT Calculator
- BMI Calculator
- Calorie Calculator
- Body Fat Calculator
- BMR Calculator
- Ideal Weight Calculator
- Lean Body Mass Calculator
- Percentage Calculator
- Area Calculator
- GPA Calculator
- CGPA Calculator
- Age Calculator
- Zakat Calculator
