Ovulation Calculator
Ovulation: Meaning, Symptoms, Cycle Calculation, Fertile Window & Ovulation Calculator Guide
Ovulation is a key biological process in the female reproductive system and plays a central role in fertility, pregnancy planning, and menstrual health. Understanding ovulation helps women track their cycles, identify fertile days, manage hormonal health, and either plan or prevent pregnancy effectively.
This detailed guide explains what ovulation is, when it occurs, symptoms of ovulation, how to calculate ovulation accurately, fertile window timing, irregular cycles, ovulation disorders, and how ovulation calculators work.
What Is Ovulation?
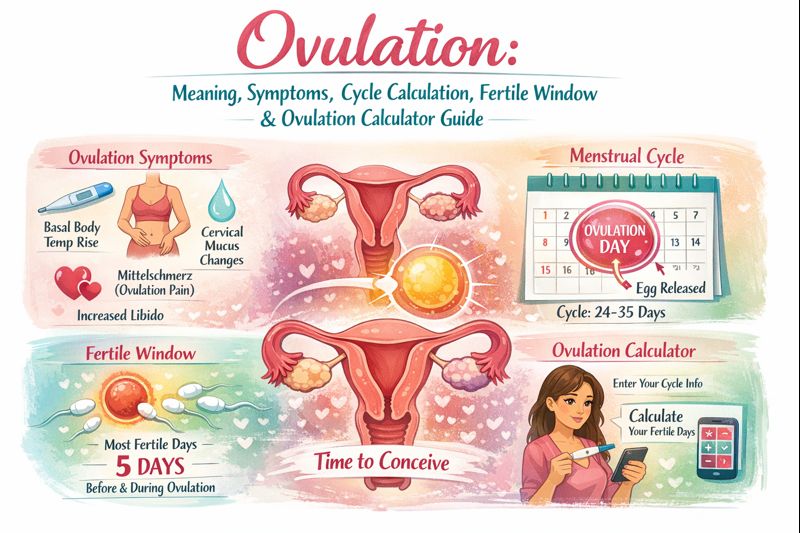
Ovulation is the process in which a mature egg (ovum) is released from one of the ovaries into the fallopian tube. This egg remains viable for fertilization for 12 to 24 hours. If sperm fertilizes the egg during this time, pregnancy can occur.
Ovulation typically happens once per menstrual cycle and is regulated by hormones such as:
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
When Does Ovulation Occur?
Ovulation usually occurs about 14 days before the start of the next menstrual period, not necessarily on day 14 of every cycle.
What Is the Fertile Window?
The fertile window is the period when pregnancy is most likely to occur. It includes:
5 days before ovulation (sperm can survive up to 5 days)
Ovulation day itself
Fertile Window Example
If ovulation occurs on Day 14, the fertile window is:
Day 9 to Day 14
This makes timing intercourse during the fertile window crucial for conception.
Signs and Symptoms of Ovulation
- Clear, stretchy cervical mucus (egg-white consistency)
- Mild pelvic or lower abdominal pain (mittelschmerz)
- Increased libido
- Breast tenderness
- Heightened sense of smell
- Slight increase in basal body temperature (after ovulation)
- Light spotting (rare)
How to Calculate Ovulation Manually
Step-by-Step Method
Determine your average cycle length
Subtract 14 days from your cycle length
The result is your estimated ovulation day
Example:
Cycle length = 30 days
30 − 14 = Day 16 (Ovulation)
This method works best for women with regular cycles.
Ovulation Date Calculator: How It Works?
An ovulation date calculator estimates ovulation and fertile days using:
First day of last menstrual period (LMP)
Average cycle length
Period duration
Ovulation and Irregular Cycles
Women with irregular cycles may experience:
Delayed ovulation
Missed ovulation (anovulation)
Inconsistent fertile windows
Causes of Irregular Ovulation
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- Thyroid disorders
- Stress
- Excessive exercise
- Weight fluctuations
- Hormonal imbalance
Ovulation Disorders and Anovulation
Anovulation occurs when the ovary does not release an egg.
Common Ovulation Disorders
PCOS
Hypothalamic dysfunction
Premature ovarian insufficiency
Hyperprolactinemia
Symptoms of Ovulation Problems
Irregular or absent periods
Difficulty conceiving
Heavy or very light bleeding
Hormonal acne or excess hair growth
Medical evaluation is recommended if ovulation is consistently absent.
Ovulation and Pregnancy Chances
Pregnancy Probability
Intercourse during fertile window: 20–30% chance per cycle
Best days: 2 days before ovulation and ovulation day
Age, sperm health, and ovulation regularity significantly affect conception chances.
Ovulation After Birth Control
After stopping hormonal birth control:
Ovulation may return within 2–6 weeks
Some women take 3 months or longer
Cycles may be temporarily irregular
Tracking cycles post-contraception helps identify ovulation return.
Ovulation After Period
Ovulation does not occur immediately after periods in most women.
Short cycles: ovulation may happen soon after menstruation
Long cycles: ovulation occurs much later
This is why fixed “safe days” are unreliable for contraception.
Ovulation is the foundation of fertility and menstrual health. Understanding ovulation timing, fertile windows, symptoms, and cycle patterns empowers women to make informed reproductive decisions. Using a reliable ovulation calculator combined with cycle awareness offers the most accurate and practical approach for pregnancy planning or natural family planning.
Popular Calculator Tools
- Period Calculator
- Loan Calculator
- Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC) Calculator
- Blood Pressure Calculator
- Pregnancy Calculator
- Conception Calculator
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Pregnancy Conception Calculator
- Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) Calculator
- Fat Intake Calculator
- Interest Rate Calculator
- Annuity Calculator
- Annuity Payout Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Sales Tax Calculator
- VAT Calculator
- BMI Calculator
- Calorie Calculator
- Body Fat Calculator
- BMR Calculator
- Ideal Weight Calculator
- Lean Body Mass Calculator
- Percentage Calculator
- Area Calculator
- GPA Calculator
- CGPA Calculator
- Age Calculator
- Zakat Calculator
