Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Calculator
Best Eye Response (E)
Best Verbal Response (V)
Best Motor Response (M)
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) Calculator – Complete Medical Guide
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) calculator is one of the most widely used neurological assessment tools in modern medicine. It plays a crucial role in evaluating a patient’s level of consciousness, especially in cases of traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, metabolic encephalopathy, infections, and other acute neurological conditions. Due to its simplicity, reproducibility, and clinical relevance, the GCS has become a global standard in emergency medicine, neurology, neurosurgery, and intensive care units.
An accurate GCS score calculator helps clinicians quickly assess brain function, determine injury severity, guide immediate management, and monitor neurological changes over time. Online tools now allow healthcare professionals and students to calculate GCS accurately while minimizing scoring errors.
History and Development of the Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale was introduced in 1974 by Sir Graham Teasdale and Bryan Jennett at the University of Glasgow. Prior to its development, assessing consciousness was inconsistent and subjective, making communication between clinicians difficult.
The GCS was designed to provide:
- A standardized neurological assessment
- Objective measurement of consciousness
- A tool that could be used repeatedly for monitoring trends
Over decades of validation, the GCS scale calculator has proven reliable across diverse clinical settings and patient populations.
What Is the Glasgow Coma Scale?
The Glasgow Coma Scale assesses three independent neurological responses:
- Eye Opening (E) – brainstem and arousal function
- Verbal Response (V) – cortical function and language
- Motor Response (M) – cortical and spinal motor pathways
Each response is scored separately and then added together to generate the total GCS score.
The GCS calculator expresses the result as:
- A total score (3–15)
- A component score (e.g., E3 V4 M5)
This breakdown provides more clinical information than the total score alone.
How to Calculate GCS Using GCS calculator
To calculate GCS, each category is scored based on the best observed response.
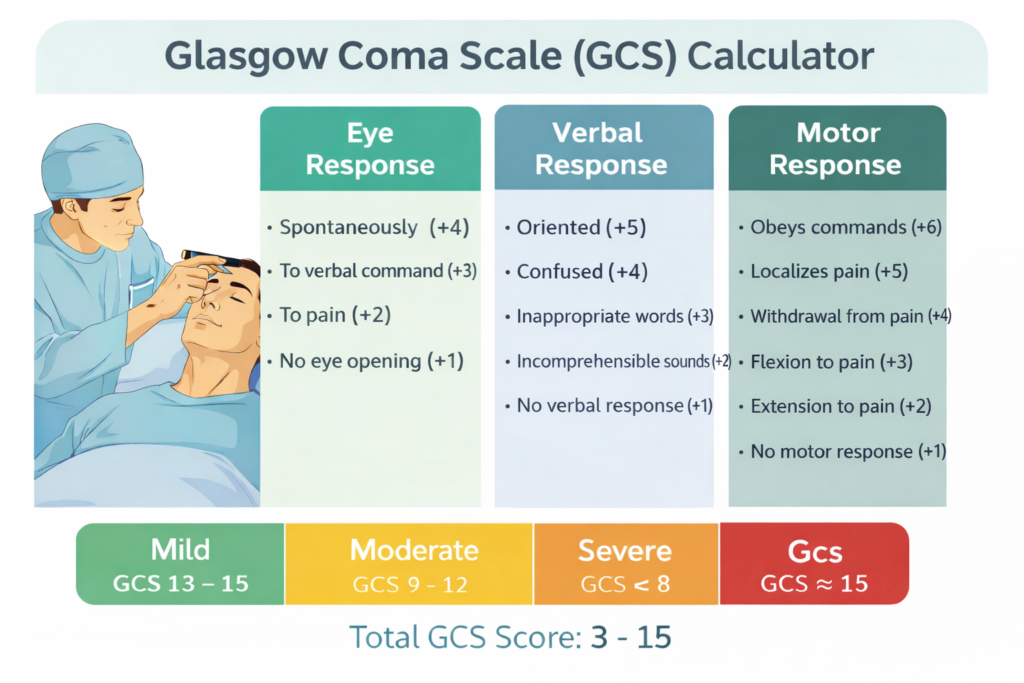
Eye Opening Response (E)
| Response | Score |
|---|---|
| Spontaneous eye opening | 4 |
| Opens eyes to verbal command | 3 |
| Opens eyes to pain | 2 |
| No eye opening | 1 |
Eye response reflects activation of the reticular activating system and overall alertness.
Verbal Response (V)
| Response | Score |
|---|---|
| Oriented and coherent | 5 |
| Confused conversation | 4 |
| Inappropriate words | 3 |
| Incomprehensible sounds | 2 |
| No verbal response | 1 |
The verbal component assesses language centers and higher cortical function. In intubated patients, verbal scoring may be recorded as “NT” (not testable).
Motor Response (M)
| Response | Score |
|---|---|
| Obeys commands | 6 |
| Localizes pain | 5 |
| Withdraws from pain | 4 |
| Abnormal flexion (decorticate) | 3 |
| Extension to pain (decerebrate) | 2 |
| No motor response | 1 |
Motor response is the most predictive component of patient outcomes and reflects integrity of both cortical and spinal pathways.
GCS Score Range and Interpretation
After scoring each component, the values are added using a GCS score calculator.
GCS Severity Classification
| Total GCS Score | Clinical Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 13–15 | Mild brain injury |
| 9–12 | Moderate brain injury |
| ≤8 | Severe brain injury / coma |
A GCS score of 8 or less is clinically critical and often indicates the need for airway protection and intensive monitoring.
Clinical Uses of GCS Calculator
The GCS calculator is essential in many medical settings:
1. Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
GCS is the primary tool for:
- Classifying injury severity
- Determining imaging requirements
- Predicting prognosis
2. Emergency Medicine
Emergency physicians use calculate GCS tools for rapid neurological triage.
3. Intensive Care Units (ICU)
Repeated GCS assessments help monitor:
- Neurological deterioration
- Response to treatment
- Sedation effects
4. Stroke and Neurological Disorders
GCS assists in assessing consciousness level in:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage
- Ischemic stroke
- Encephalitis and meningitis
Importance of Using an Online GCS Calculator
Manual scoring can be affected by:
- Stressful environments
- Time pressure
- Human error
An online gcs scale calculator ensures:
- Accurate score calculation
- Clear E-V-M breakdown
- Consistent interpretation
- Faster clinical decision-making
This is especially useful for medical students, paramedics, nurses, and clinicians.
Pediatric and Special Considerations
While the standard GCS is validated for adults, special considerations apply in:
- Children
- Intubated patients
- Sedated or paralyzed patients
In such cases, clinicians may mark components as not testable and use modified pediatric scales.
Limitations of the Glasgow Coma Scale
Despite its widespread use, the GCS has limitations:
- Does not assess brainstem reflexes
- Verbal score cannot be assessed in intubated patients
- Less sensitive to subtle neurological deficits
- Affected by drugs, alcohol, and sedation
Therefore, clinicians should always use the GCS alongside clinical judgment and additional neurological examinations.
Prognostic Value of GCS
Lower GCS scores are strongly associated with:
- Increased mortality
- Poor neurological outcomes
- Longer ICU stays
The motor score is particularly valuable for predicting outcomes and trauma guidelines often emphasize it.
Medical Disclaimer
This GCS calculator is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It should not replace professional medical assessment, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for clinical decision-making.
Conclusion
The Glasgow Coma Scale calculator remains a cornerstone of neurological assessment worldwide. By enabling clinicians to quickly and accurately calculate GCS, it supports timely intervention, improves communication, and enhances patient safety. Whether used in emergency care, intensive care, or education, a reliable gcs score calculator is an essential clinical tool.
Popular Calculator Tools
- BSA Calculator
- Period Calculator
- Ovulation Calculator
- Blood Pressure Calculator
- Pregnancy Calculator
- Conception Calculator
- Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Pregnancy Conception Calculator
- Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) Calculator
- Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) Calculator
- Corrected Calcium Calculator
- Creatinine Clearance Calculator
- eGFR Calculator
- Anion Gap Calculator
- BMI Calculator
- Calorie Calculator
- Body Fat Calculator
- BMR Calculator
- Ideal Weight Calculator
- Lean Body Mass Calculator
